AIAA Rotorcraft Hover Prediction Workshop (HPW)
AIAA Applied Aerodynamics Technical Committee
HVAB Rotor Test Case
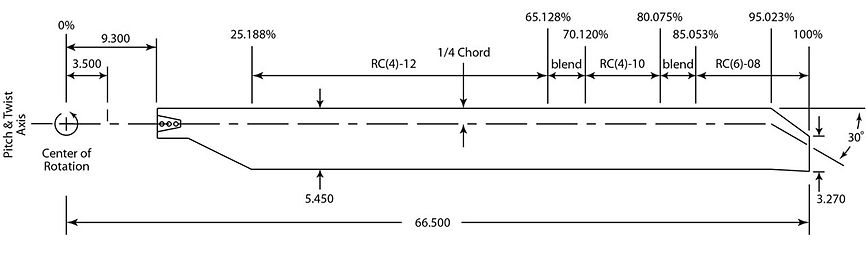
HVAB Rotor Description
Blade Number..................................................... 4
Radius......................................................... 66.5 in
Solidity....…………...............................………. 0.1033
Reference Chord.........................................5.45 in
Tip Chord.................................................... 3.27 in
Tip Sweep................................... 30 deg at 95% R
Flap Hinge..................................................... 3.5 in
Rotor Speed......................................1250.39 RPM
Tip Mach Number............................... 0.65 @ SLS
Conditions
Calculations should be performed for a tip Mach
number of 0.65 assuming standard day sea level
conditions. To allow for direct comparison to
experimental data and with other's results it is
recommended that the investigators cover the
range of collective angles from 6 to 10 degrees.
Assuming coincident flap and lead/lag hinge locations,
expected coning and lag angles are reported below.
Collective Cone Lag
6° 0.4° 1.9°
8° 0.8° 2.5°
10° 1.3° 3.4°
12.76° 2.0° 5.0°
Structural Properties
The structural properties of the PSP and HVAB rotor differ significantly. HVAB properties are documented in NASA-TM-2020-5002153 located in the reference section below. Please note that in Section 4 the shear center, center of gravity, and tension center are reported relative to the blade coordinate system and NOT relative to the local airfoil coordinate system. Also, The units of chord inertia on page iv and in Tables 20, 21, 23 and 24 are lbf s^2, not lbf s^2 in^2 or lbf s^2 in.
HVAB vs. PSP Rotor
While the HVAB blades have the same OML as the PSP blades for the outer .75R, they are not exactly the same. There are three primary differences:
-
While the rotor diameters are identical, the blades themselves (from hub attachment point to tip) are slightly different; this is due to the use of different hubs with different attachment points;
-
The HVAB blades are designed for a trailing edge thickness of 0.0350” vs. the PSP thickness of 0.0300” (both are design values);
-
The root fairing (used to cover wiring and connectors inboard of 25% radius) has a slightly different shape.
HVAB Test Data
https://rotorcraft.arc.nasa.gov/HVAB
References
Surface Geometry
Surface geometry and volume grid of the HVAB rotor blade is available on the FileShare page in plot3d format